What Is A Fowler's Position
position
[pŏ-zish´united nations]one. a actual posture or attitude.
two. the relationship of a given betoken on the presenting function of the fetus to a designated point of the maternal pelvis; encounter accompanying table. See also presentation.

Common test positions. From Lammon et al., 1995.
anatomical position that of the human body standing cock, palms facing forward; information technology is the position of reference in designating site or management of structures of the body. The anatomical position for quadrupeds is standing with all four feet on the footing; the difference between animal and human anatomical position leads to confusion amid terms indicating position and direction.

The torso in the anatomical poisition, showing regions of the body. From Applegate, 2000.
batrachian position a lying position of infants in which the lower limbs are flexed, abducted, and resting on the bed on their outer aspects, resembling the legs of a frog.
Bozeman's position the knee joint-elbow position with straps used for back up.
decubitus position that of the body lying on a horizontal surface, designated according to the aspect of the body touching the surface equally dorsal decubitus (on the dorsum), left or right lateral decubitus (on the left or right side), and ventral decubitus (on the anterior surface). In radiology, the patient is placed in either the right or left lateral decubitus position with the beam perpendicular to the long centrality of the body.
dorsal recumbent position position of patient on the back, with lower limbs flexed and rotated outward; used in vaginal examination, awarding of obstetrical forceps, and other procedures. See illustration.
Fowler's position a position in which the caput of the patient'southward bed is raised 30 to 90 degrees higher up the level, with the knees sometimes also elevated. See illustration.
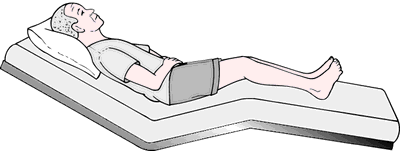
Low Fowler's.
knee-chest position the patient rests on the knees and breast with head is turned to one side, arms extended on the bed, and elbows flexed and resting so that they partially carry the patient's weight; the belly remains unsupported, though a pocket-sized pillow may exist placed under the chest. Run into illustration.
articulatio genus-elbow position the patient resting on the knees and elbows with the chest elevated.
lithotomy position the patient lies on the dorsum with the legs well separated, thighs acutely flexed on the belly, and legs on thighs; stirrups may exist used to support the feet and legs. See illustration.
orthopneic position a position assumed to relieve orthopnea (difficulty breathing except when in an upright position); the patient assumes an upright or semivertical position by using pillows to support the head and chest, or sits upright in a chair.
decumbent position a position with the patient lying face downwards with artillery aptitude comfortably at the elbow and padded with the armboards positioned forward.
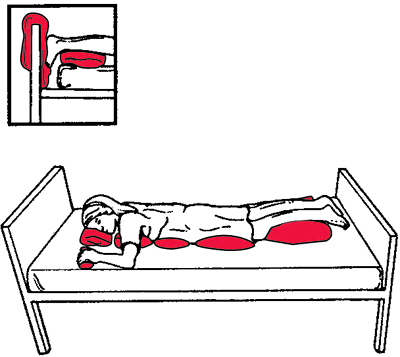
Prone position. From Lammon et al., 1995.
reverse Trendelenburg position a supine position with the patient on a plane inclined with the head college than the rest of the body and advisable rubber devices such every bit a footboard.
Rose's position 1 intended to prevent aspiration or swallowing of blood, as from an injured lip: the patient is supine with caput hanging over the end of the table in total extension so every bit to enable haemorrhage to be over the margins of the inverted upper incisors.
semi-Fowler position a position similar to Fowler's position but with the head less elevated.
Sims position the patient lies on the left side with the left thigh slightly flexed and the right thigh acutely flexed on the abdomen; the left arm is behind the body with the torso inclined forward, and the right arm is positioned according to the patient's comfort. See analogy. Chosen also lateral position.
Sims recumbent position a variant of the Sims position in which the patient lies on the left side in a modified left lateral position; the upper leg is flexed at hip and knees, the lower leg is straight, and the upper arm rests in a flexed position on the bed.
Trendelenburg's position the patient is on the back on a table or bed whose upper section is inclined 45 degrees so that the head is lower than the residuum of the body; the adjustable lower section of the tabular array or bed is aptitude then that the patient's legs and knees are flexed. There is back up to keep the patient from slipping. Meet illustration.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Lexicon of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, 7th Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is A Fowler's Position,
Source: https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Fowler%27s+position
Posted by: matterfinge1992.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is A Fowler's Position"
Post a Comment